My take on the latest developments in IT companies, IT and Software Engineering, Project Management experiences, reflections on PMBOK, critiques on Project Management books. Nerd Alert! :)
Thursday, December 26, 2013
Value Stream Mapping Current state map markup and Future state map for a call center
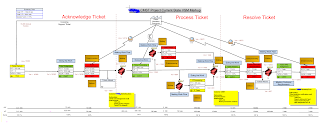
The next step in Value Stream Mapping is the Markup for the current state map. At this step, the bottleneck areas are identified in the current value stream map. As shown in the diagram below for the call center value stream map, a markup is created by identifying the bottlenecks at each step of the ticket resolution process. The type of bottleneck is also identified at this step such as Overprocessing, Defect, Waiting etc. These bottlnecks need to be removed and the process needs to be stream lined.
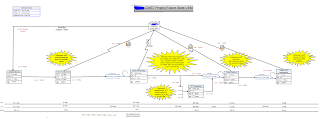
The last step in Value Stream Mapping is the Future State Mapping. In this step, the bottlenecks identified in the current state map markup are removed and the future streamlined process is documented as a diagram. The star bursts indicate the process improvements. The flow of the entity through the process is recorded. The volume of entities processed at each step of the process is also documented. Here is a sample future state diagram for a BPO call center that I created from a project that I worked on where "ticket" is the entity that passes through the process. The potential ticket volumes are recorder at each step. If you do not have the exact volumes, use a best guess estimate. The processing time and lead times are measured and calculated for each step. Click on the future state map image below to see full size image. This diagram was created using Microsoft Visio. Please leave any questions in the comments section below.
The last step in Value Stream Mapping is the Future State Mapping. In this step, the bottlenecks identified in the current state map markup are removed and the future streamlined process is documented as a diagram. The star bursts indicate the process improvements. The flow of the entity through the process is recorded. The volume of entities processed at each step of the process is also documented. Here is a sample future state diagram for a BPO call center that I created from a project that I worked on where "ticket" is the entity that passes through the process. The potential ticket volumes are recorder at each step. If you do not have the exact volumes, use a best guess estimate. The processing time and lead times are measured and calculated for each step. Click on the future state map image below to see full size image. This diagram was created using Microsoft Visio. Please leave any questions in the comments section below.
Monday, December 23, 2013
Capstone Project - Infosys China - Strategic Analysis
For my capstone project, I chose Infosys Technologies Limited, and did a strategic analysis of Infosys' decision to expand in China. The strategic analysis includes a background of Infosys Ltd, customer segments, geographic scope, timeline of the decision to expand in China, Macro-environment as well as Internal environment of the company in terms of its vision, mission, financial position and competitive advantage.
Executive Summary
Infosys Technologies Limited, is adopting an
aggressive expansion strategy in China, with a proposed investment of $125-150
million to set up its own state-of-the-art campus in Shanghai to build up
service delivery capabilities and serve the local market. Infosys has
traditionally been averse to acquisitions, held its premium pricing strategy
and focused on its core IT enabled services business. However, the recent
changes in the corporate leadership in 2011 and slowdown in growth, have
prompted a strategic shift towards global expansion and moving up the value
chain with consulting and technology partnership. The Chinese expansion
decision comes at a time when Infosys is making a strategic shift towards global
expansion through acquisitions and partnerships.
Infosys considers China as a potential market as
well as potential resource pool for the company's global aspirations. Increasing
competition with other multinationals for skilled IT professionals, soaring
salaries in India and an emerging Chinese market were the main reasons for
entering China as a low-cost center. However, China also presents significant
challenges in terms of economic slowdown, political/legal issues such as
government regulations and intellectual property protection, socio-cultural
issues such as high attrition rates and low availability of English-speaking
professionals, and increased domestic and international competition for labor
and clients.
Infosys must look to expand in China as it is an
important emerging market; most of its clients and other multinational
companies are also moving into China and Infosys should not lose this
opportunity. It should leverage its competitive advantage to attract employees
and support its growth, but also keep a close watch on the external environment
in China.
I.
Overview of the Business
A. Company
Background
Infosys is a global consulting and an Information
Technology (IT) Service Company, headquartered in Bangalore, India. It went
public in India in 1993 and got listed on the United States of America (USA)
NASDAQ in 1999. Infosys Limited was founded in 1981 by Narayana Murthy and six
other people. Murthy, who was the CEO from 1981 and became the Chairman in
2002, retired in 2011 upon turning 65, and is now the Chairman Emeritus at Infosys.
Infosys, most famously under the leadership of N.R. Narayana Murthy and Nandan
Nilekani, came to define an industry that symbolizes modern entrepreneurial
India, with legions of young workers converging on its Silicon Valley-style
campuses[1]. Co-founder and chief
operating officer S.D. Shibulal is the current CEO. Infosys has more than
153,000 employees. From a capital of US$ 250, Infosys has grown to become a US$
7.126 billion (LTM Q2 FY13 revenues) company with a market capitalization of
approximately US$ 28 billion.
B. Industry(s)
in which company competes
Infosys competes in
the Software and Information Technology Services and Consulting industry and
focuses on providing IT expertise, software design, development and maintenance
services as well as on-site management and other IT functions to its customers.
Driven by strong demand of IT infrastructure in developing economies, the
global information technology industry is expected to grow at a rate of 5.88%
during the period 2011-2015, according to a report by global research firm
TechNavio[2].
C. Customer
segments served
Infosys offers
business technology consulting, IT services and IT solutions in major
industries such as Aerospace & Defense, Airlines, Automotive, Communication
services, Energy, Financial services, Healthcare, High-tech, Hospitality and
leisure, Insurance, Life sciences, Logistics and distribution, Manufacturing, Media
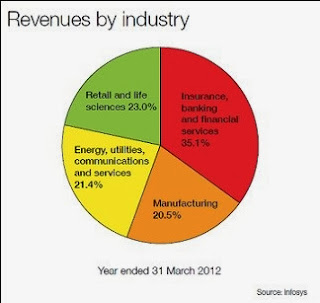
& entertainment, Public sector, Retail and Utilities Industry. As shown in
the following chart, the revenues are almost equally distributed across its
five major customer segments.
D. Products/services
offered
Infosys provides end-to-end IT solutions which
include software application development, testing and maintenance, business
process management, infrastructure management and product engineering services.
During the financial crisis, many companies cut down on IT costs. Infosys realized
that in order to have sustainable growth, the company needs to move up the
value chain and not simply be a low cost IT service provider.
Infosys has been shifting its strategy to increasingly
offer platform and product solutions, which are geared towards providing much
more value to its clients, getting more clients and delivering high value
product and services in a cost effective way. Some of the popular products from
Infosys are Finacle – Universal Banking Solution, Infosys Care Suite and
Infosys Real-time Expertise Manager – Customer service products, Infosys Supply
Chain Performance Management Suite, and SpeedSolve – Chat-based customer
support product. Infosys also offers a suite of business platforms called “Infosys
Edge”, that helps businesses simplify digital marketing, multi-channel
commerce, manage IT asset performance, increase
employee engagement and accelerate long term growth and profitability[3].
Following is a graphical representation of Infosys
revenue from product services offered in FY 2011. A bulk of the revenue is
based on application development and maintenance of existing applications for
its clients.
E. Geographic
scope of the business
The Infosys brand has moved out of India. Infosys
has a global footprint with offices and development centers in 77 cities spread
across 32 countries from Americas, Asia Pacific, Europe, Middle East and
Africa. A bulk of the revenue is generated from managing the back-office
computer systems of multinational companies in the US and Europe as shown in
the following chart[4].
The company continues to expand at a great pace and is scouting for
acquisitions in 'all geographies' to expand its overseas footprint.
F. Business
level strategy
The business model of Infosys is based on the Global
Delivery Model (GDM), which takes advantage of the company’s global presence in
delivering value to clients. Infosys pioneered the Global Delivery
Model (GDM), based on the principle of taking work to the location where
the best talent is available, where it makes the best economic sense, with the
least amount of acceptable risk. Continued leadership around GDM enables
Infosys to drive extraordinary efficiencies and free up clients’ resources for
strategic transformation or innovation initiatives[5]. This means not only is Infosys becoming
a global brand, but it also has the capability to support the global operations
of multinational clients.
The company’s global presence allows its clients
certain benefits which include the ability to work around the clock and
business continuity. For example, if the client has working hours from 9 to 5
in the USA, the next shift picks up in India after 5pm in America and works
when the USA office is closed. It also saves the customer from any disruption
to its business in the event of say a natural disaster, as the business
operations just get picked up by another location not affected by the disaster.
From the beginning, Infosys focused on
“differentiation” strategy through innovation and quality and positioned itself
as a premium IT service provider compared to its peers in the Indian IT
services industry. In line with this, it also enjoyed higher margins of 25-30%
as compared to its peers such as Wipro, TCS and Cognizant[6]. However,
compared to its other global competitors such as Accenture, Deloitte and IBM,
Infosys is a “low-cost” service provider.
II.
Description and Brief Discussion of the
Strategic Decision
A. Strategic
Decision
Recently, Infosys announced the expansion of its
offices in China. Infosys is planning on establishing its own development
center campus in Shanghai, Hangzhou and Beijing that can accommodate about 8000
employees, a sales office in Hong-Kong and a global education center in
Jiaxing, with a proposed investment of $125-150 million. Infosys BPO, the
business processing outsourcing arm of Infosys, is also setting up a new center
in Dalian, China, with a 500-person capacity[7].
Though most Indian software firms have face difficulties in the Communist
country, Infosys believes it’s all about perseverance and intends to hire 2,000
more employees, despite attrition rate climbing to an unusually high 20%[8].
In this paper, I will analyze Infosys’s strategic decision to expand operations
in China and examine the strengths and weaknesses of Infosys as an organization
as well as the opportunities and threats to Infosys as it pursues expansion in
China.
B. Time
line and Timing of the Decision
Infosys established its first BPO centre in China in
2006. The decision to expand operations in China was announced in the late 2011
after 5 years of operating in China. Construction for the new projects has
already begun. And when completed, the new centres will undertake projects in
software development, IT services and IT-enabled services, and will also act as
one of the training and research centres of the company. Infosys has big plans
for China and sees it as a potential market for it to grow in terms of new
clients and customers, and the low-cost high-skilled labor acts as a attractive
source for the company to expand and setup new development centers outside
India.
III.
External Environment (Opportunities and
Threats):
A. Macro-environmental
forces
1.
Economic
One of the reasons that encouraged Infosys to enter
China in the early 2000s was the rapid growth of the Chinese economy which had
attracted several multinationals, many of which were clients of Infosys. However
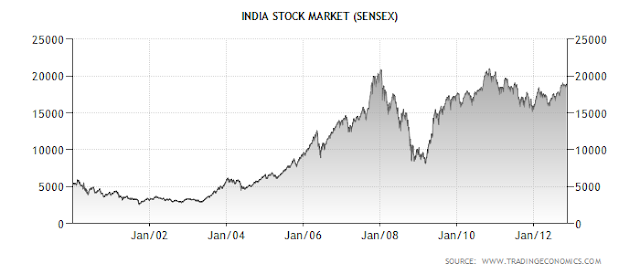
in recent years, there has been an economic slowdown in China; while India’s stock market has soared in
recent years, the opposite has happened in China.
China’s
GDP growth rate has also been declining in the last ten years. Infosys will
need to closely monitor the economic situation in China in the coming years.
2.
Political/Legal
The political
environment in China also presents a higher degree of difficulty in conducting
business as compared to India. India has a more laissez-faire attitude in both
politics and business. China, being a communist nation, has greater regulation
and involvement. Infosys had a first-hand experience of Chinese government
regulation concerning the ownership structure, repatriation of profits and the
shareholding pattern, when it first tried to establish a branch office and was
given permission to set up a joint venture with the government[9].
Infosys was against the joint venture as both parties would have conflicting
agendas; government with its political agenda of creating jobs and acquiring
knowledge, and Infosys with its agenda for maximizing profit. Infosys then
established a representative office and started working towards obtaining
permission to establish a development center. These issues had delayed Infosys'
Chinese venture but eventually Infosys set up Infosys Technologies (China) Co.
Limited as a wholly-owned subsidiary in 2003 and Infosys Technologies
(Shanghai) Co. Limited as a wholly-owned subsidiary in 2011.
The legal environment
in China also poses a risk for Infosys in terms of Intellectual Property
protection. Like India, the intellectual property laws are present, but not
strictly enforced which results in software piracy and copyright infringement
issues. When working with multinational clients in China such as banking,
financial services or insurance, Infosys will need to strictly enforce
governance standards to ensure intellectual property and sensitive data
protection.
3.
Sociocultural
Chinese programmers
tend to have limited English-language skills are better equipped to understand
and analyze material written in Chinese and to customize programs for the
Chinese market. Infosys will need to invest in language and technical training of
the employees to cater to multinational companies. Although the labor costs in
China are lesser compared to India, Chinese employees are unlike Indian
employees. Infosys has an extremely high attrition rate in China because the Chinese
believe a 10-12% annual raise is not good enough[10]. Infosys will need to find
alternate ways to engage the Chinese employees and get return on investment for
its training and maintain its profit margin.
4.
Technological
The foreign companies
entering China are looking at established players in the software industry, who
could understand systems, technologies, procedures and standards in China, and
Infosys does not want to miss this high potential business opportunity. The
market for software and IT services in China is expected to grow exponentially
and according to Gartner, Indian IT companies are expected to account for 40%
of this market.
B. Industry
and Competitive Environment
1.
Existing Competitors
Infosys is competing
globally with other Indian IT companies such as TCS, Wipro, HCL Technologies,
and Cognizant for clients as well as human resources. The 2011 global market
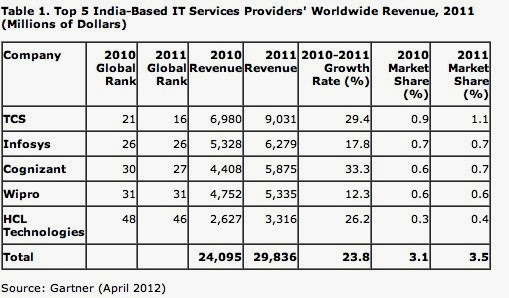
share of its competitors is as presented below.
The most important
reason for entering China was the soaring salaries of software professionals in
India - a result of growing global demand for them[11]. With an increasing number
of international firms such as IBM, Microsoft, Accenture, and Deloitte
competing with Infosys for hiring from the same pool of software engineering
professionals, the gap between the demand and availability of skilled manpower
in India was likely to increase further, and India was estimated to witness a
shortage of 250,000 workers in the IT industry by 2009, according to a study
conducted by KPMG and NASSCOM. However, Infosys will still face intense
competition in China from domestic software companies as well as foreign
competitors who are also trying to expand Chinese operations, many of whom have
entered China much before Infosys. However, China is undergoing a huge
industrial revolution and is an important emerging market with a strong talent
pool.
2.
Threat of Substitute Products or Services
Infosys provides a
range of proprietary products and support services that can be customized to
suit the business needs of its clients across multiple domains such as banking,
retail and insurance as described earlier. However, similar bespoke products
and services are also provided by its global competitors as well as domestic
competitors in China, so there is a higher threat of substitute products and
services with lower switching costs. Infosys has been known to acquire
long-term project contracts with its clients in US and UK. In China, due to the
highly competitive domestic software services industry that is vying for
foreign clients, Infosys will need to price the projects right in order to gain
long-term contracts[12].
3.
Bargaining Power of Buyers
Due to the presence
of a large number of domestic and international IT companies in China the
bargaining power of its customers has increased. Also multinational companies
may prefer to switch to domestic IT and consulting companies to leverage the
local knowledge.
4.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers
Infosys has to
compete for skilled-labor with the global and domestic IT companies in China as
well, which increases the bargaining power of its suppliers, who are mainly
software and IT engineers. Software companies are known to poach employees by
providing a “joining bonus”. This may eventually drive up wage levels, just
like in India, making it more difficult to attract and retain employees.
5.
Barriers to Entry
The Chinese
government regulations present significant barriers to entry to international
IT companies. However, there are relatively lower barriers to entry to domestic
IT companies, except in terms of technological infrastructure requirements.
IV.
Internal Environment (Strengths and Weaknesses):
A. Mission
Infosys’s Vision and Mission are important drivers
of its strategic decisions. The vision statement “We will be a globally
respected corporation” reflects its intent for going global and expanding
globally. The mission statement “Strategic Partnerships for Building Tomorrow’s
Enterprise” reflects a desire to acquire or partner with the right company with
complementary expertise. Infosys Chief Executive Officer and Managing
Director S. D. Shibulal articulates his vision of the smart
enterprise by focusing on “emerging economies” as one of the key drivers of
business. In light of these views, the decision to expand into China clearly
supports Infosys’s mission of becoming a global enterprise.
B. Financial
Position
Reviewing the financial statements of Infosys at the
time it entered China, Infosys' global revenues increased by 33.5% from
Rs 71.3 billion in the financial year 2004-05 to Rs 95.2 billion in the
financial year 2005-06. However, its Chinese subsidiary had incurred loss of Rs
166 million on revenue of Rs 260 million. The reason for this loss, Infosys
said, was that though it was able to secure some local clients, it was unable
to attract foreign companies operating in China to procure its services[13]. By
altering its premium pricing strategy and leveraging its competitive advantage
with existing multinational clients in China, Infosys has been able to gain a
sturdy financial position in China and has been listed as the Top 10 global
service providers in China by the China council for International Investment
Promotion[14].
Infosys is in a strong financial position with
revenue of more than $6 billion in 2011. Infosys has been consistently enjoying
not only financial success but also a very high price-equity ratio that gives
it an excellent valuation on the stock markets and a blue chip status. This
implies that it has the capital to expand, and also the basis to leverage
potential investors. Infosys hopes that its Chinese operations would contribute
10% of its total revenues by 2015[15].
C. Sources
of Competitive Advantage
Infosys has a
strong brand recognition in the IT industry in India and abroad. It was the
first Indian company to list on a US Stock Exchange. It is ranked among the 50
most respected countries in the world by Reputation Institute’s Global Pulse
2009. It has also been voted most admired Indian company in the Wall Street
Journal Asia since 2000. The strong brand identity would definitely help
Infosys in attracting employees as well as new clients in China. Many of
Infosys’s existing clients have moved into China, and they might prefer to
continue their strategic IT alliance with Infosys to leverage existing
knowledge and keep learnings within the company. Having Infosys located in
China, will give the proximity advantage for customer service that Infosys
maintains with its on-site client locations.
Infosys China
office has been operational since eight years and has served as an additional
base for global customers. The time zone difference between the western
countries and China will help Infosys leverage its Global Delivery Model
effectively. The low labor-cost advantage will also help Infosys in maintaining
its profit margins and differentiation strategy while providing value-creation
products and services to its clients.
Infosys has a comprehensive
portfolio of solutions as well as IT quality standard certifications such as
CMM Level 5i and Six Sigma expertise to differentiate from domestic competitors
in China. Infosys also has excellent infrastructure, telecommunication
facilities and the capability of global 24/7 delivery through its development
centers in other locations, which gives it a competitive advantage over the
domestic competitors.
Infosys has been
awarded the No. 1 spot globally for its corporate governance practices and No.
2 spot for its financial disclosures policies by IR Global Rankings (IRGR).
IRGR is the most comprehensive technical ranking system for investor relations
websites, corporate governance practices and financial disclosure procedures[16].
This will definitely provide Infosys a competitive advantage compared to other
IT companies in China, which has a weak legal structure.
Despite being a
huge IT company compared to its Indian competitors such as TCS, HCL, Wipro and
Cognizant, Infosys is much smaller than its global competitors such as IBM, HP
and Accenture. Infosys generated $6 billion in 2011, which is relatively low in
comparison with large global competitors such as Hewlett-Packard ($91 billion),
IBM ($91 billion), EDS ($21 billion) and Accenture ($18 billion)[17].
Also, Infosys’ Chinese office has been operational for only eight years, so it
has relatively less experience in China than some of its other international competitors.
Infosys has also
been struggling with high attrition rates of 14.9% in 2012 due to wage-hike
issues. These attrition numbers are thrice as much as the general industry rate[18].
Infosys will need to revamp its human resource strategy in China to prevent a
high attrition and retain its resource knowledge and capabilities within the organization.
Infosys does not
have experience with acquisitions and has traditionally been averse to acquisitions;
its first acquisition was Lodestone Holding AG in Switzerland in October 2012. There
is a significant learning curve from incorporating another company, especially
when the parent company has a strong corporate culture. As Infosys plans
aggressive expansion in China through acquisitions, it should look to find a
suitable company with a similar corporate culture to avoid any culture clashes
that create disharmony within the organization.
D. Corporate
Governance
In the last ten
years, after founder Narayan Murthy stepped down as CEO, Infosys has had four
CEOs, with each of the co-founders taking a shot at leading the company. This
has affected the company’s growth and critics say that Infosys is overly
focused on service delivery and not enough on sales; that it is slavish to
preserving margins at the expense of winning new business[19]. Infosys’s
new CEO S.D. Shibulal who took over in 2011 is the main driver behind the
strategic shift towards global expansion through acquisitions.
E. Corporate
Culture
Infosys has a
strong corporate culture, where each employee is treated as part of the Infosys
family and referred to as “Infoscion”. It invests in its employees with a
long-term goal and trains them to become global employees, so as to facilitate
easy movement of resources between different development centers and client
locations. It is common for employees to rotate between on-site client
locations and off-shore development centers. Customer-centric focus is a strong
part of the corporate culture and the company urges its employees to work
towards “customer delight” and not simply “customer satisfaction”. Infosys’
approach in China is also with a long-term view of obtaining skilled resources
to join the Infosys “family” and work towards creating a strong skilled labor
base.
F. Code
of Ethics
Infosys is a
highly respected IT company that considers ethics critical to its business
strategy. Although Infosys is targeting China mainly for low-cost labor, it is
focused on delivering long-term value to its employees, shareholders and
society[20]. Many manufacturing companies like Nike are
known to take advantage of the low-cost labor in China through sub-contractors,
which can cause labor law violations and worker exploitation. Infosys is
known to invest heavily in training its employees to support the long-term
goals of the company and not exploiting its employees for short-term gains.
Infosys’ long-term goals in China are evident from the $125-150 million investment in establishing its own campus in
Shanghai versus subcontracting to local IT companies in China.
V.
Global Ethics and Social Responsibility
Considerations
Infosys has been
consistently viewed as the most transparent and ethical organization by the
customers, employees, society and the investor community. Infosys's founder and
Chairman Emeritus, Narayanamurthy, has always been a great follower and
advocate of ethics in business. While a number of organizations today are
engaged in window-dressing their accounts and also are trying to communicate a
performance far better than the actuals, with a view to inflating their
valuation, Infosys always followed the policy of naked transparency in front of
the investing community, through their ' When in doubt, disclose' approach[21]. Infosys
was ranked among 'India's Best Companies to Work For - 2009' in a survey by the
Great Place to Work® Institute India in collaboration with The Economic Times.
Infosys featured among the best companies for large organizations and corporate
social responsibility.
VI.
Final Conclusion and Summary
With the slowing
growth rate in the last ten years in US and Europe due to economic slowdown, a
turbulent corporate leadership at Infosys, growing pressure from the
shareholders, the increasingly competitive skilled-labor situation and soaring
salaries in India and an emerging market in China, I think Infosys’ China
expansion is a need of the hour. However, Infosys will need to keep
[1]
Arakali, H., & Chatterji, S.
(2012, May 7). Infosys woes prompt calls for change at top| Reuters. Business & Financial
News, Breaking US & International News | Reuters.com.
Retrieved December 15, 2012, from http://www.reuters.com/article/2012/05/07/us-india-infosys-idUSBRE84606420120507
[2]
Global information technology market
to grow by 5.88% until 2015: TechNavio - Computer Business Review. (2012, May
15). IT
Services Industry News - Services - Computer Business Review.
Retrieved December 14, 2012, from http://itservices.cbronline.com/news/global-information-technology-market-to-grow-by-588-until-2015-technavio-150512
[3]
Infosys Products and Platforms.
(n.d.). Infosys - Business Technology Consulting | IT
Services | Enterprise Solutions. Retrieved December 14,
2012, from http://www.infosys.com/products-and-platforms/Pages/platforms.aspx#platforms s
[4]
Supplier profile: Infosys. (n.d.). ComputerWeekly.com.
Retrieved December 14, 2012, from http://www.computerweekly.com/guides/Supplier-profile-Infosys
[5]
Infosys - About the Company. (n.d.). Infosys - Business Technology
Consulting | IT Services | Enterprise Solutions.
Retrieved November 13, 2012, from
http://www.infosys.com/about/Pages/index.aspx
[6]
Is it time Infosys cut prices?
(2012, September 10). Business Standard.
Retrieved December 14, 2012, from http://www.business-standard.com/india/news/is-it-time-infosys-cut-prices/485837/
[7]
Mishra, B. R. (2011, December 28).
Infosys BPO to expand in China. Business Standard.
Retrieved November 12, 2012, from http://www.business-standard.com/india/news/infosys-bpo-to-expand-in-china/459980/
[8]
Hector, D. J. (2012, March 13).
Infosys to hike China head count, retain best workers.Financialexpress.com.
Retrieved January 4, 2012, from http://www.financialexpress.com/news/infosys-to-hike-china-head-count-retain-best-workers/923032/
[9]
Infosys in China. (2006). IBS Center for Management
Research. Retrieved December 14, 2012, from http://www.icmrindia.org/casestudies/catalogue/Business%20Strategy/Infosys%20in%20China.htm
[10]
Hector, D. J. (2012, March 13).
Infosys to hike China head count, retain best workers.Financialexpress.com.
Retrieved January 4, 2012, from http://www.financialexpress.com/news/infosys-to-hike-china-head-count-retain-best-workers/923032/
[11]
Infosys in China. (2006). IBS Center for Management
Research. Retrieved December 14, 2012, from http://www.icmrindia.org/casestudies/catalogue/Business%20Strategy/Infosys%20in%20China.htm
[12]
Fung, E. (2011, September 15).
Infosys China CEO: Will Continue to Expand Organically - WSJ.com. The Wall Street Journal.
Retrieved December 14, 2012, from http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424053111904060604576572211692441924.html
[13]
Infosys in China. (2006). IBS Center for Management
Research. Retrieved December 14, 2012, from http://www.icmrindia.org/casestudies/catalogue/Business%20Strategy/Infosys%20in%20China.htm
[14]
Infosys ranked among the Top 10
Global service providers in China. (2012, July 13). Infosys Press Release.
Retrieved December 15, 2012, from http://www.infosys.com/newsroom/press-releases/Documents/2012/global-service-providers-award.pdf
[15]
Infosys in China. (2006). IBS Center for Management
Research. Retrieved December 14, 2012, from http://www.icmrindia.org/casestudies/catalogue/Business%20Strategy/Infosys%20in%20China.htm
[16]
Infosys - Corporate Governance
Practices | IR Global Rankings. (n.d.). Infosys.
Retrieved December 15, 2012, from http://www.infosys.com/newsroom/press-releases/Pages/corporate-governance-practices.aspx
[17]
Infosys SWOT. (n.d.). Marketing Teacher.
Retrieved December 14, 2012, from http://www.marketingteacher.com/swot/infosys-swot.html
[18]
Iyer, S. (2012, July 16). Infosys
attrition number is the real shocker | Firstpost. Latest News: Breaking/Live
News Today, Latest News India, Politics News, Business/Stock Market News,
Sports Updates, Bollywood News and Opinions - Firstpost.com.
Retrieved December 14, 2012, from http://www.firstpost.com/business/infosys-attrition-number-is-the-real-shocker-378976.html
[19]
Fung, E. (2011, September 15).
Infosys China CEO: Will Continue to Expand Organically - WSJ.com. The Wall Street Journal.
Retrieved December 14, 2012, from http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424053111904060604576572211692441924.html
[20]
Code of Conduct. (n.d.). Infosys.
Retrieved December 15, 2012, from http://www.infosys.com/investors/corporate-governance/Documents/CodeofConduct.pdf
[21]
Srinivas (2012, July 30). Secrets of
Successful Organizations..: BENCHMARK FOR BUSINESS ETHICS- INFOSYS & &
TATA GROUP. Secrets of Successful Organizations..
Retrieved December 15, 2012, from http://mastermentorsadvisory.blogspot.com/2012/07/benchmark-for-business-ethics-infosys.html
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)